Technology has always been a driving force in the money transfer industry. From the early days of telegraphic money orders to the current digital landscape of online banking and mobile apps, each new development has made sending money around the world more accessible and faster.
The latest innovation to disrupt the money transfer industry is blockchain technology. Blockchain is best known as the underlying technology behind the digital currency Bitcoin, but its potential uses extend far beyond cryptocurrency. Let’s look closely at how blockchain eats into the money transfer market.
How Do International Money Transfers in the US Compare To Bitcoin?
Money transfers have dominated the international payments landscape for decades. In the United States, the two leading players are Western Union and MoneyGram.
While money transfers remain the most popular way to send money internationally, Bitcoin has been gaining ground in recent years. It currently accounts for a small fraction of the international money transfer market, but the number is expected to grow.
The only reason Bitcoin hasn’t taken over the international money transfer market is the sophistication technology that’s needed to use it. However, as blockchain technology becomes more mainstream, that will likely change.
In the future, money transfers may well be made using blockchain technology. This would have several advantages over the current system.
What Are the Advantages of Blockchain Money Transfers?
The main advantage of using blockchain for international money transfers is that it dramatically reduces the cost of sending money abroad.
When sending money internationally, the transaction has to go through several intermediaries, including banks and other financial institutions. Since these middlemen all charge fees for their services, the charges are passed on to the customer through higher transfer fees.
With blockchain, there would be no need for these middlemen. Transactions would be processed directly between two parties without needing a third party to handle it. This would reduce the cost of sending money internationally, making it more affordable for individuals and businesses.
Another advantage of blockchain money transfers is that they would be much faster than traditional money transfers. It can take days or even weeks for an international money transfer to be processed, but with blockchain, you can complete the process in a matter of minutes.
This would be a huge advantage for businesses that need to send money abroad regularly. It would also benefit individuals who need to send emergency funds to family or friends in another country.
Finally, blockchain money transfers would be much more secure than traditional ones. With traditional methods, there is always the risk that hackers could steal your personal or financial information. With blockchain, your information would be stored on a decentralized network of computers, making it virtually impossible to hack. This would give you peace of mind knowing that your money is safe and secure.
How Could This Affect Money Transfer Fees?

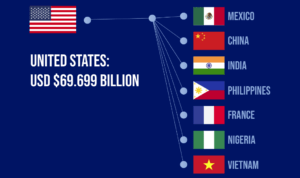
International money transfers still dominate the digital world, but the blockchain is slowly eating into its market share. According to Money transfer data via this comparator site, money transfer transactions in the US alone hit $69.699 billion. This is a lot of money and will only grow as blockchain technology becomes more mainstream.
Forbes reports that the average cost of an international money transfer is about 6%. This means that, on average, it costs $6 to send $100 from one country to another.
While this may not seem like a lot, it can add up quickly, especially if you send more significant amounts of money. For example, if you send $1,000 from the US to Europe, you would pay $60 in fees.
With blockchain money transfers, the fees would be much lower. This is because there would be no need for intermediaries, such as banks and other financial institutions. Banks could potentially lose a lot of revenue if blockchain money transfers became the norm.
This would be good news for consumers, as it would lower the cost of sending money internationally. However, it could harm the revenue of banks and other financial institutions. Only time will tell how this will play out.


































